Brolucizumab is a single-chain antibody fragment,30,31 which at 26 kDa is a much smaller molecule than both aflibercept (97–115 kDa) and ranibizumab (~48 kDa).32,33 With a clinical dose of 6 mg and around 11 to 13 times the number of molecules per injection compared with aflibercept, brolucizumab has more VEGF-binding ability per volume compared to other currently available anti-VEGF agents.30-33 Brolucizumab has been specifically engineered to achieve more drug in a single injection, potent inhibition of VEGF-A, effective penetration of the retina and choroid, and rapid systemic clearance.28,30,34
The efficacy and safety of brolucizumab for the treatment of nAMD was compared with that of aflibercept in the phase 3 HAWK and HARRIER trials (Figure 7).28,35 HAWK and HARRIER were double-masked, multicenter, active-controlled, randomized trials in which patients in the brolucizumab arm received three monthly injections of 3-mg (HAWK) or 6-mg (HAWK and HARRIER) brolucizumab followed by dosing every 12 weeks which was adjusted to 8-weekly dosing if disease activity was detected.28 Patients in the aflibercept arm received 2-mg aflibercept every 8 weeks following three loading doses. “An assessment at week 16 permitted a matched comparison with identical treatment exposure between study arms,” said Mr. Hamilton. The primary endpoint of non-inferiority in mean BCVA was at week 48, with the study ending at 96 weeks.28
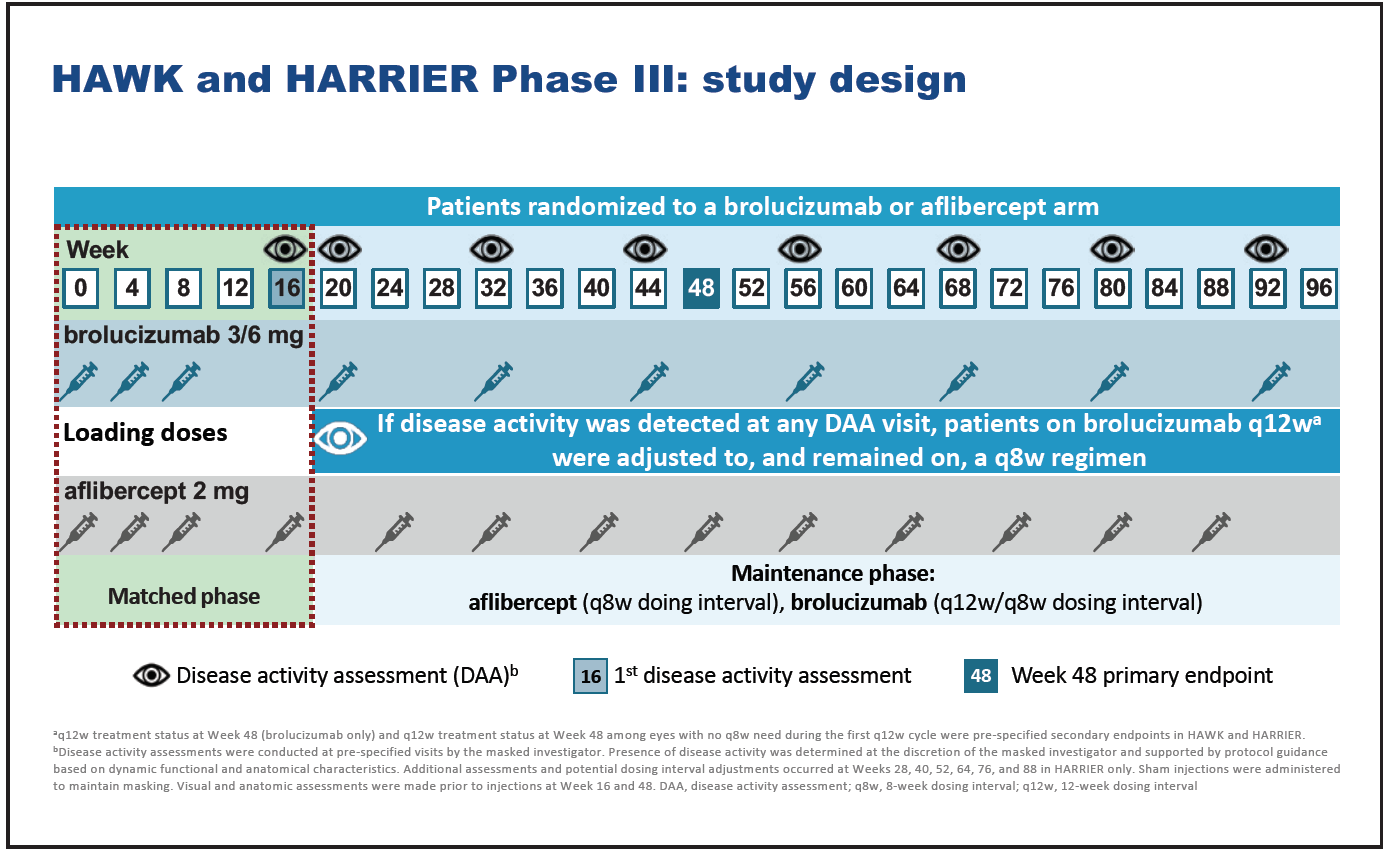
Figure 7. HAWK and HARRIER study design.
The primary endpoint of BCVA noninferiority was met in both HAWK and HARRIER (Figure 8). In HAWK, least squares mean VA gains were 6.6, 6.1, and 6.8 letters for 6-mg brolucizumab, 3-mg brolucizumab, and 3-mg aflibercept, respectively. In HARRIER, least squares mean VA gains were 6.9 and 7.6 letters for 6-mg brolucizumab and aflibercept, respectively.28 VA gains were maintained to week 96 in both trials.

Figure 8. Change in BCVA from baseline to week 96 in HAWK and HARRIER.
Over 50% of brolucizumab 6-mg patients were maintained on a 12-week dose interval from the end of the loading phase until week 48,28 and over 75% of brolucizumab 6-mg patients who completed week 48 on a 12-week dose interval remained on that interval until week 96.35
In terms of anatomical outcomes, patients in the brolucizumab arm achieved significantly greater reductions in central subfield thickness compared with aflibercept from baseline to weeks 16 and 48,28 and this difference remained at week 96 (Figure 9).35 Significantly fewer patients in the brolucizumab arms had intraretinal and/or subretinal fluid at weeks 16, 48, and 96, compared with aflibercept (Figure 10).28,35 Also, fewer patients in the brolucizumab arms had sub-RPE fluid at these timepoints, compared with aflibercept.28,35
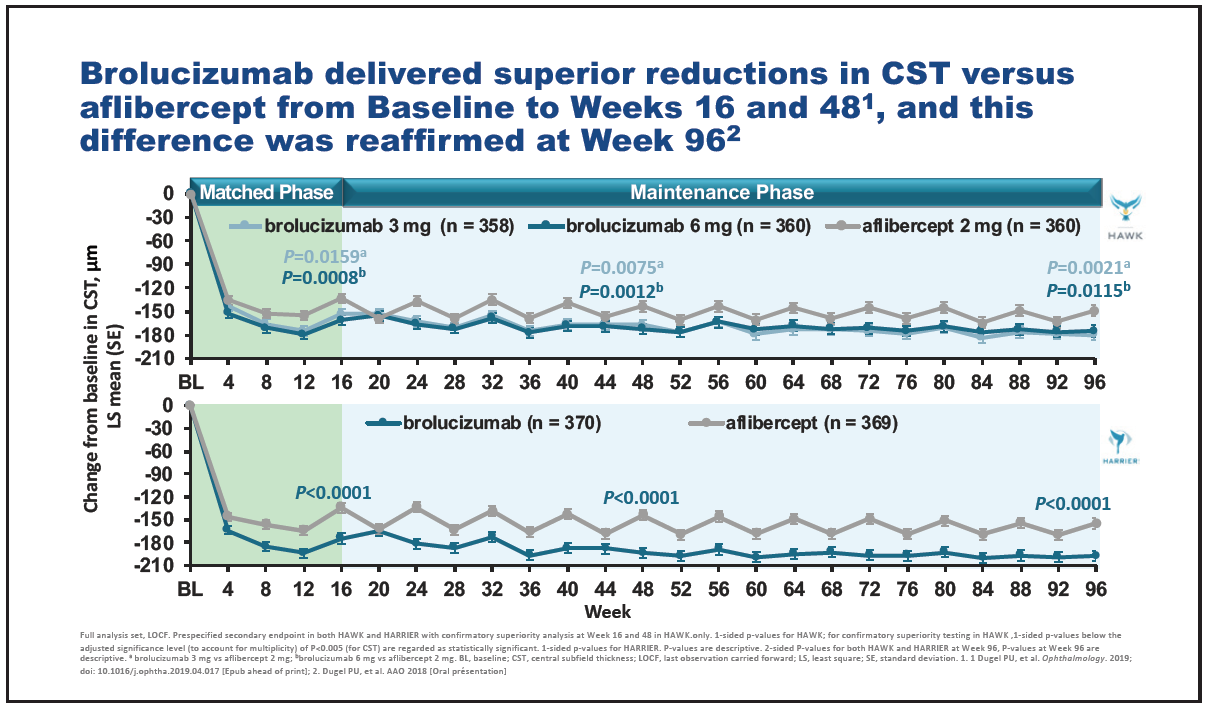
Figure 9. Change in central subfield thickness over time in HAWK and HARRIER.

Figure 10. Patients with intraretinal and subretinal fluid at weeks 16, 48, and 96 in HAWK and HARRIER.
Disease activity was assessed by a masked investigator. At week 16, significantly fewer patients given 6-mg brolucizumab were judged as having disease activity compared with aflibercept (Figure 11).28 Brolucizumab exhibited an overall well-tolerated safety profile.
Post-marketing cases of IOI, vasculitis, and retinal occlusive vasculitis in relation to use of brolucizumab have been reported, as noted in reports issued by the American Society of Retina Specialists (ASRS) to its members. These AE reports are being investigated by Novartis, who established an external Safety Review Committee (SRC) to complete an independent post-hoc review of all cases of investigator-reported IOI, retinal vascular occlusions and endophthalmitis in the phase 3 HAWK and HARRIER studies. The SRC has provided a report of their unmasked, independent analysis, which can be downloaded from www.brolucizumab.info. As further assessments continue, updated information will be provided to the medical community by Novartis on a regular basis on this website.

Figure 11. Disease activity assessment at week 16 in HAWK and HARRIER.
Further clinical evidence comparing brolucizumab with aflibercept will be provided by TALON, a randomized, double-masked, phase 3b, multicenter study.36 “Unusually, TALON is a superiority study, which is designed to determine whether brolucizumab allows longer intervals than aflibercept in an identical 4-week adjustment treat-to-control regimen in patients with nAMD,” said Mr. Hamilton. “According to the investigator’s judgement of disease activity, the treatment interval can be extended to a maximum of 16 weeks or a minimum of 4 weeks.” The treat-to-control regimen is designed to reflect clinical practice and determine the optimum treatment interval for each patient based on disease status (Figure 12). The focus is on sustaining disease control rather than on extending the treatment interval as is the case with treat-and-extend (T&E) regimens. “In clinical practice, some patients may benefit from being maintained on a certain treatment interval or require a reduced interval in order to control disease activity,” said Mr. Hamilton.
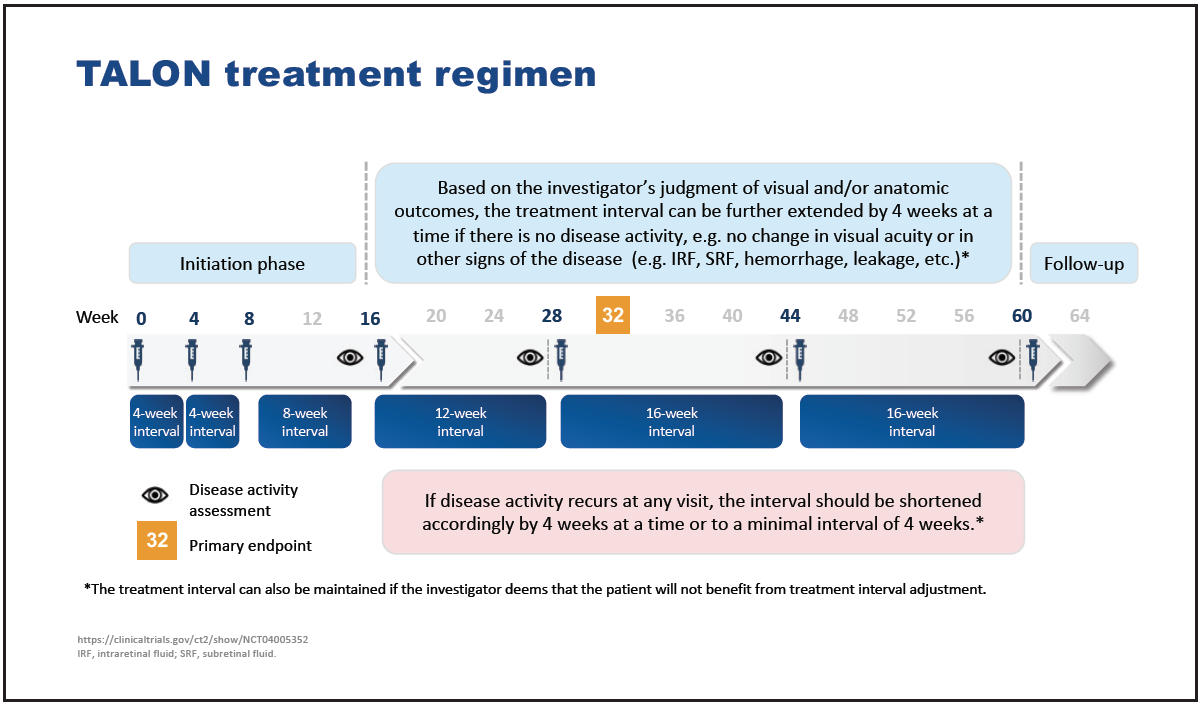
Figure 12. TALON treatment regimen.
In conclusion, in HAWK and HARRIER, brolucizumab demonstrated noninferiority to aflibercept in terms of BCVA gain at week 48 and superiority to aflibercept on anatomical outcomes. Successful completion of 48 weeks at a 12-week interval was highly predictive of continuing on a 12-week interval to the end of the study. The upcoming TALON study will evaluate the efficacy and safety of 6-mg brolucizumab compared with 2-mg aflibercept in a treat-to-control regimen.
Highlights
- In HAWK and HARRIER, BCVA outcomes achieved with brolucizumab at week 48 were reaffirmed at week 96, and the superior anatomic results seen for 6-mg brolucizumab at weeks 16 and 48 were also seen at week 96.28
- In HAWK and HARRIER, over 50% of brolucizumab 6-mg patients were maintained on a 12-week dose interval until week 48.28 Successful completion of a 12-week interval at week 48 was highly predictive of continuing on 12-weekly intervals up to week 96.35
- The TALON study will evaluate the efficacy and safety of 6-mg brolucizumab compared to 2-mg aflibercept in a treat-to-control regimen.36
